Deutsch: Chirurgie / Español: Cirugía / Português: Cirurgia / Français: Chirurgie / Italiano: Chirurgia /
Surgery in the quality management context doesn't directly correlate as a term commonly used within the traditional scopes of quality management principles or frameworks like ISO 9001. However, if we interpret "surgery" in a broader sense related to quality management, especially within healthcare or medical device manufacturing sectors, it can be understood as the high level of precision, care, and adherence to stringent quality standards and protocols required in surgical procedures and the production of surgical equipment.
Application to Healthcare Services
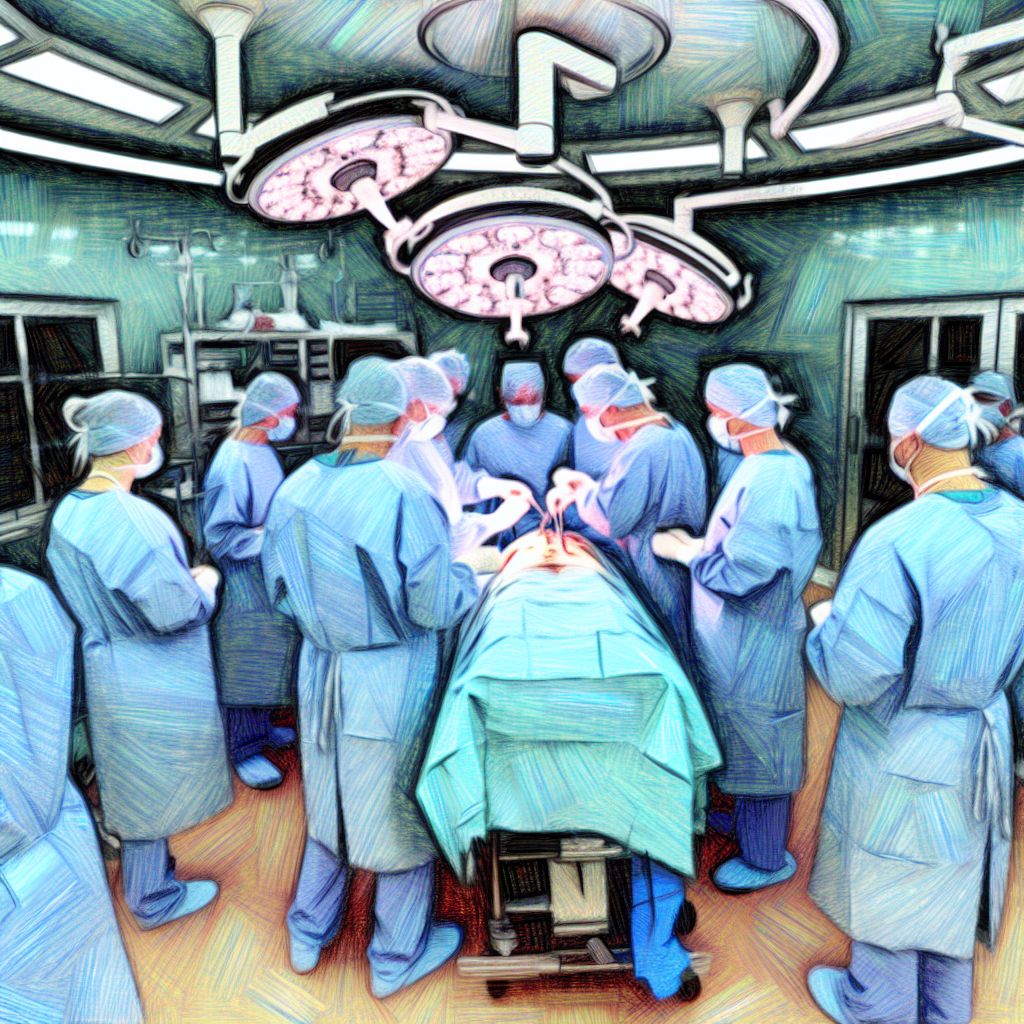
In the healthcare services context, surgery involves critical patient care activities that demand meticulous planning, execution, and post-operative management to ensure patient safety and successful outcomes. Quality management in this context focuses on:
- Standardization of Surgical Procedures: Implementing evidence-based protocols to guide surgical interventions, ensuring consistency and minimizing risks.
- Sterilization and Cleanliness: Maintaining strict sterilization processes for surgical instruments and environments to prevent infections.
- Qualification and Training: Ensuring surgeons and surgical staff are highly qualified, well-trained, and continuously updated on best practices and innovations.
- Patient Safety and Satisfaction: Monitoring patient outcomes, managing risks, and gathering patient feedback to improve surgical care.
Application to Medical Device Manufacturing
In the context of manufacturing medical devices, including surgical equipment, surgery emphasizes the importance of designing and producing devices that meet rigorous quality and safety standards. This involves:
- Precision Manufacturing: Producing devices with the precision and reliability required for surgical applications, where even minor defects can have significant consequences.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to regulatory standards such as those set by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) or EMA (European Medicines Agency) for medical devices, ensuring they are safe and effective for surgical use.
- Quality Control and Testing: Implementing comprehensive quality control measures and conducting extensive testing to validate the performance and safety of surgical devices.
- Traceability and Accountability: Maintaining detailed records of device manufacturing processes, materials, and distribution to ensure traceability and accountability.
Weblinks
- psychology-lexicon.com: 'Surgery' in the psychology-lexicon.com
- medizin-und-kosmetik.de: 'Chirurgie' im Lexikon von medizin-und-kosmetik.de (German)
Summary
While surgery itself is not a term traditionally used within quality management frameworks, the principles of quality management are critically applicable to surgical practices and the production of surgical equipment. Ensuring high standards of quality and safety is paramount in these areas, given the direct impact on patient outcomes and well-being. Quality management practices in these contexts are geared towards standardizing procedures, ensuring competency, maintaining cleanliness and sterilization, and producing reliable and safe surgical equipment.
Related Articles to the term 'Surgery' | |
| 'Compatibility' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■■■ |
| In the psychology context, compatibility refers to the degree to which two individuals are able to coexist . . . Read More | |
| 'Calibration' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■■■ |
| Calibration is a significant Concept in psychology, primarily related to the Assessment and Adjustment . . . Read More | |
| 'Dose' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■■■ |
| Dose is defined as the amount of drug or exercise prescribed to have a certain effect or response. Dose . . . Read More | |
| 'Standard' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■■■ |
| Standard is a level or Grade of excellence regarded as a Goal or measure of adequacy. Standard in the . . . Read More | |
| 'Edition' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■■ |
| Edition in the Psychology Context: Understanding, Examples, and RecommendationsUnderstanding Edition . . . Read More | |
| 'Audit' at top500.de | ■■■■■■■■ |
| Audit in the industrial or industry context refers to a systematic Examination of a company’s accounts, . . . Read More | |
| 'Strain' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■ |
| Strain in psychology refers to the mental, emotional, or physical Stress experienced by an individual . . . Read More | |
| 'Setup' | ■■■■■■■■ |
| Setup in the quality management context refers to the preparation, configuration, or organisation of . . . Read More | |
| 'Disclosure' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■■ |
| Disclosure means sharing Information with others about whether one is gay, lesbian, or bisexual. In psychology, . . . Read More | |
| 'Procurement' at psychology-lexicon.com | ■■■■■■■ |
| In the context of psychology, procurement does not directly relate to traditional psychological theories . . . Read More | |
